The cURL library is ideal and complete for anyone who wants to make requests or transfer data through the backend of their applications. With cURL, in addition to simple requests such as GET and POST, it is possible to make requests using other protocols such as FTP, POP, IMAP, and others.
Before we start, we have to call the function that will make our development work.

Configuring in practice
When we start the cURL resource, we can use parameters that will configure our request. Below are some important parameters:
– CURLOPT_RETURNTRANSFER – Returns a string
– CURLOPT_CONNECTTIMEOUT – Seconds trying to connect until timeout
– CURLOPT_TIMEOUT – Limit seconds for cURL execution
– CURLOPT_USERAGENT – String containing a user-agent
– CURLOPT_USERAGENT – String containing a user-agent
– CURLOPT_PORT – Port report
– CURLOPT_HTTPHEADER – Request headers
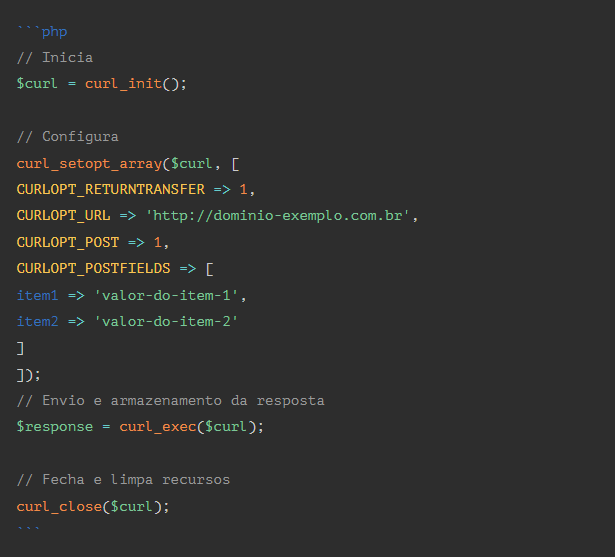
– CURLOPT_POST – Send the request as POST
– CURLOPT_POSTFIELDS – Information array sent as POST
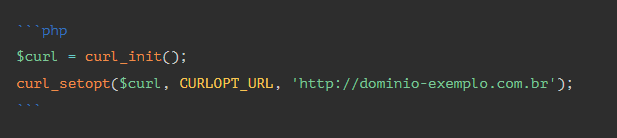
To inform a parameter, we must use the curl_setopt() function and, if necessary, we can send more than one parameter using the curl_setopt_array() function, as in the examples below:
Example 01:
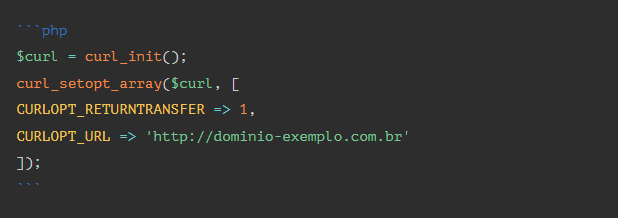
Example 02:
SHIPPING
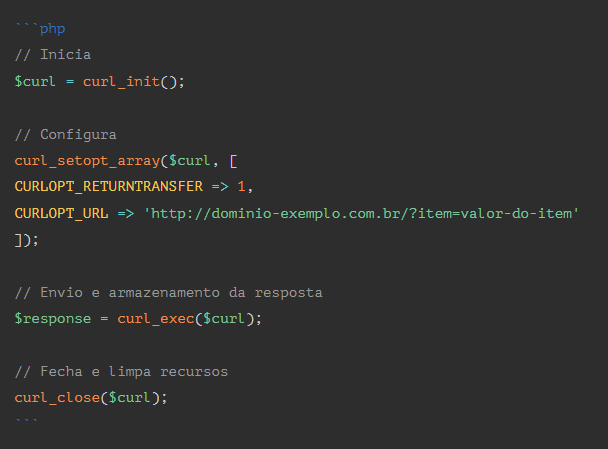
Now, that we understand how to configure our submission, let’s use the curl_exec() function that execute our submission. When sending, we can come across two responses, false, which refers to when there is an error in the execution of the request, and true, which occurs when making a request.
In addition to the functions and results presented above, it is important that, when the request ends, the cURL is closed to clean up the resources currently being used. And for that, I have prepared examples below that you can copy and paste into your application if you need to.
EXAMPLE: GET
EXAMPLE: POST
ERROR RETURNS
Over time you will become familiar with the library, and with that, you will begin to identify which errors can happen and should be treated, for this, you can use the functions curl_error() (returns in string format) and curl_errno() (returns in code format).
With this knowledge, you will be able to explore and use RESTful APIs in several projects and mobile applications efficiently, as the largest companies in the world use today.


















Leave a comment